What causes an allergic reaction?
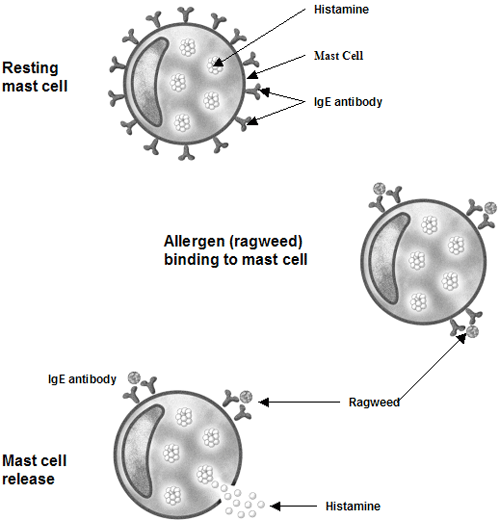
Mast cells line the mucous membranes of the nose, sinuses and lungs ready to release histamine and other chemical mediators, which can cause inflammation of the nose, sinuses and bronchial tubes. In allergic reactions, the allergy antibody, IgE, serves as the bridge between allergic substances and the mast cells. When allergens bind to IgE on the mast cell surface, they release chemicals. In other circumstances, mast cells release their chemicals without an allergic trigger (such as following a cold). The effects of mast cell mediator release depends on where the reaction occurs. For example, if mast cell release occurs in the eye, you could experience symptoms of eye allergies; if release occurs in the nose or sinuses, you could experience symptoms of hayfever; if the reaction occurs in the lungs, you could experience asthmatic symptoms. The reactions in all of these areas is caused by the accumulation of various cells, swelling and increased mucous production.