Mediator Release
The chemically-rich mast cells that line the bronchial mucous membranes may release histamine or other chemical mediators, which can cause bronchospasm and bronchial inflammation. In
allergic asthma, the allergy antibody, IgE, can cause the mast cells to release chemicals when exposed to appropriate allergen(s). In other circumstances, mast cells release their chemicals without an allergic trigger (e.g. following a cold or with exercise).
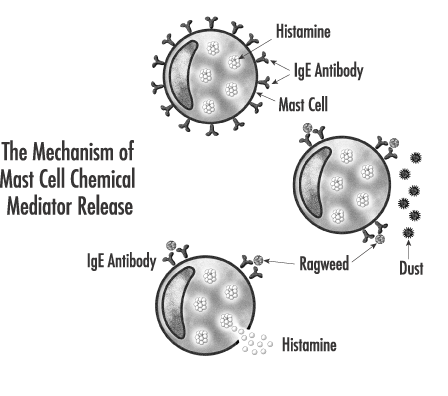
If you are asthmatic, the effects of the mast cell mediator release are:
- Spasm of the smooth muscle surrounding the airway Inflammation
- Swelling of mucous membranes within the bronchi
- Increased mucus production within the bronchi
This process not only produces asthmatic symptoms but also increases the hyper-responsiveness of the bronchial tubes to other irritant and/or allergen exposure(s).